Research
I am an Action on Hearing Loss Pauline Ashley Fellow mentored by Guy Richardson. My current project uses both zebrafish and mouse cochlear cultures to understand how aminoglycoside antibiotics are trafficked in sensory hair cells. Aminoglycoside’s are used in clinical practise to treat life-threatening bacterial infections but as an unfortunate side effect, they can cause the damage and loss of sensory hair cells from the inner ear resulting in deafness and balance disorders. They do this by entering the cells through the channels in the top of the hair cells or via vesicles that normally carry essential materials into the cell. Once inside they cause a chain reaction resulting in the death of the cell. How these antibiotics are trafficked though the hair cell is poorly understood, to advance our knowledge I’m investigating a class of small vesicle transport proteins called RabGTPases which serve as master regulators of cell trafficking. Identifying the transport pathways taken by these antibiotics will hopefully allow us to manipulating these pathways and therefore modulate aminoglycoside toxicity.
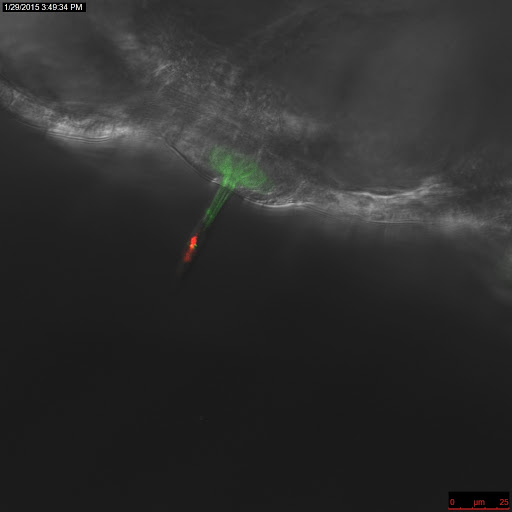
Confocal image of neuromast of Brn3c-GFP transgenic zebrafish larvae
Previous projects as Sussex have used zebrafish larvae to screen libraries of small molecules to identify candidates that can be used as therapeutics to protect cells from chemical insult. In particular, we screened over 10,000 compounds for their ability to protect zebrafish lateral line hair cells from the toxic effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Zebrafish make an ideal model for this research as they lay hundreds of transparent eggs overnight that develop rapidly so that by four-days post fertilisation the majority of the organs and tissues are developed including the lateral line hair cells. These hair cells are similar to those found in the mammalian inner ear but because they are located on the surface of the larvae the drugs can readily access the tissue without the need to dissect and culture before screening.

Images of 4 day post fertilisation zebrafish larvae. Left Image: Brightfield image of 3 zebrafish larvae. Middle Image: Fluorescent image of zebrafish lateral line cells (neuromast) labelled with FM1-43fx. Right Image: Close up fluorescent image of zebrafish neuromast labelled with FM1-43

